A Quick Guide to Material Handling Systems
Productivity is a challenge within the construction and manufacturing industry. Increasing productivity within the construction and manufacturing space means increasing the efficiency by which processes run. One way to do this is by adopting material handling equipment meant to help with handling products and materials within a facility. Using these systems of equipment facilitates the handling of products more efficiently without stretching the budget to add more manpower, hence increasing productivity.
Material handling comprises more than 20% of the U.S economy and is relevant even in today’s ongoing Covid-19 pandemic. With the production of Covid-19 vaccines, ample manufacturing capacity is required which means that any manufacturing plant needs to scale up its processes and make them more efficient.
Therefore, material handling solutions are very important in today’s economy and with this comes the need to understand how to incorporate material handling equipment to any logistics or manufacturing project.
Here is a guide to material handling systems.
What is material handling?
Material handling refers to the movement, storage, control, and protection of materials and products in manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, consumption, and disposal. This process is normally useful in retail stores, warehouses, manufacturing plants, or in any facility where heavy or bulk materials are transported.
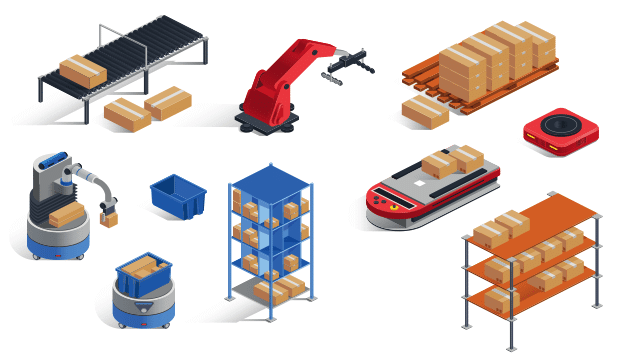
There are different types of material handling equipment based on the needs of the project. These types can be classified into 4 categories:
1. Storage and Handling Equipment
Storage and handling equipment are non-automated equipment that hold the materials when they are not being transported. The duration in which they hold these materials could either be short-term or long-term depending on the needs of the facility. For example, some materials are held at manufacturing facilities before they are shipped to their destination.
Using such equipment not only increases efficiency but also maximizes space utilization on the production floor. The increase in efficiency comes from the ease of material access. Storage and handling equipment helps the production team quickly access the materials and products they need and transport them as needed.
Examples of these equipment include:
- Racks– there are different types such as sliding racks and pallet racks. They save floor space and keep materials accessible
- Shelves, bins, and drawers– these are commonly used as storage solutions. They help with storing smaller materials
- Stacking frames– these are a stackable form of equipment that can be used to save space without damage to the products
- Mezzanines– these are elevated platforms installed between the production floor and ceiling to provide more space on the manufacturing floor. They can be movable and free-standing
2. Engineered/Automated Systems
Unlike storage and handling equipment, engineered systems are often automated. They are generally made of several units and help with storage and transportation of materials.
A popular example of an engineered equipment is an Automated Storage & Retrieval System (AS/RS) also called AS-RS or ASRS. ASRS is designed to buffer, store, retrieve product and inventory on demand. This system, just like other engineered systems, is advantageous in that it automates low-value and easily repeated tasks of inventory storage and retrieval
Other examples of engineered or automated systems include:
- Conveyer systems– Conveyer systems such as automated conveyer belts use integrated automation to move materials around the manufacturing facility with little manual effort
- Automated guided vehicles– these are mobile robots or computer-operated trucks set to move along predetermined pathways to move large materials around the warehouse.
- Robotic delivery systems– these are automated systems that help move products along assembly lines or around the manufacturing floor
3. Industrial Trucks
Industrial trucks are often used to transport heavy materials or large quantities of materials around the manufacturing floor. Industrial trucks come in various sizes and forms depending on the need of the facility. Some industrial trucks are small enough to be hand-operated and some are big enough to be driven.
Other variations include:
- Stacking trucks used to transport and load products
- Non-stacking trucks used only for transportation and not loading
- Powered industrial trucks that have a cab making it easier for the operator to pick up heavy materials
- Power-assisted trucks lift materials using manual means and have to be pushed into position but can also be operated via controls
Some examples of industrial trucks include:
- Side loaders– these are specialized vehicles that can work in the narrowest of aisles making them ideal for facilities with aisles that are close together
- Walking stackers – they operate like forklifts but do not have a place for the operator to ride in
- Hand trucks– these are also referred to as dollies. They have two wheels, a handle and a ledge on which to set boxes and are manually operated
- Platform trucks– these are hand trucks with wider platforms and sit low to the ground. Unlike hand trucks, they come in both manual and electrical forms
- Order pickers– these lift operators off the ground to higher hard to reach storage shelves or materials
- Pallet jacks– often manually pushed, they are used to move things around the manufacturing floor. They are considered a very basic form of forklifts
4. Bulk Material Handling
As the name suggests, bulk material handling is used for storing, controlling, and transporting materials in bulk.
Some examples of bulk material handling equipment include:
- Conveyer belts– automated conveyer systems are considered both engineered systems and bulk material handling; they usually move materials across the warehouse on the conveyer belt
- Stackers– often automated, stackers will move products onto stockpiles
- Reclaimers– these are large machines used to pick materials from stockpiles
- Bucket and grain elevators– often called a grain leg, these machines move bulk materials vertically
- Silos– these are towers used to hold materials (such as grains which is why they are hence often used on farms)
- Hoppers– these are shaped like funnels and are used to discharge materials into containers
Understanding material handling systems is helpful when it comes to picking the right equipment for any manufacturing plant. The type of manufacturing in the plant will determine the material handling equipment used.
To learn more about other issues facing the construction industry, check out our article highlighting 5 problems facing EPC companies.

READY TO SAVE TIME & MONEY WITH BUNDLED CABLE?
Get a quote on our custom cable bundles today.


